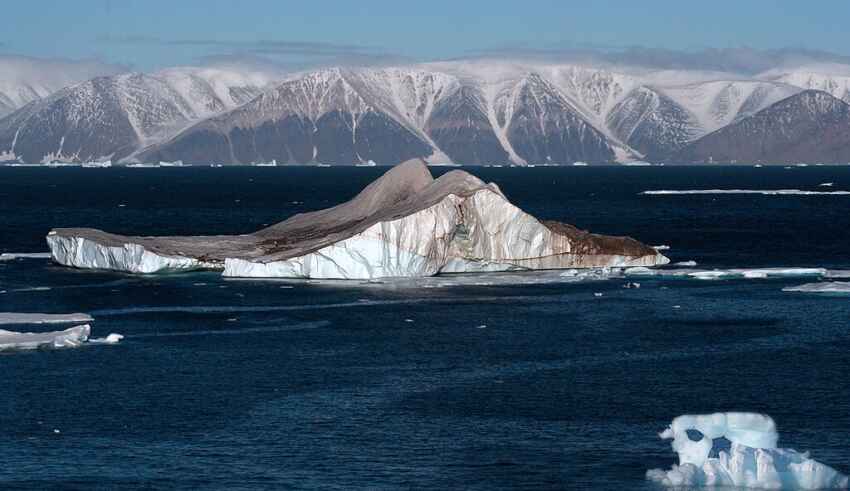
Climate change, competition for natural resources, and strategic military positioning are the driving force behind the Arctic’s rapid transformation into a major geopolitical battleground. Due to global warming, the ice sheets in the arctic continue to recede, which has made previously inaccessible regions easier to reach and exploit. At the centre of this international development sits Svalbard, an archipelago under Norwegian sovereignty governed by the 1920 Svalbard Treaty that is heavily sought after by Russia. Recent intelligence reports seem to indicate that Russia is expanding its presence in the region and potentially militarizing the area under the pretense of economic interests, which is raising concerns for Western allies and NATO as this could undermine Norwegian sovereignty and pose a greater threat to European security.
Svalbard’s geopolitical significance comes from its rich and valuable mining resources, in particular the abundance of coal in the territory. Under the Svalbard Treaty, which grants Norway sovereignty over the islands, signatory states such as Russia, are afforded equal rights to carry out economic activities including mining and fishing in the area. However, Norway’s strict enforcement of its environmental and regulatory measures are currently severely limiting Russia’s ability to execute its activities in Svalbard, which has caused significant dissatisfaction in Moscow. Additionally, given that climate change is quickly melting away the ice that covers the Arctic, new shipping routes such as the Northern Sea Route are becoming increasingly more commercially viable, thus, making Svalbard even more strategically important. The situation is also particularly troubling due to the strategic and military concerns involving control over the region. Even though the Svalbard Treaty prohibits any sort of military activity, many in the international community worry that Russia is concealing its strategic expansion behind its supposed economic interests. In that regard, Russia’s broader Arctic strategy seems to include increasing military infrastructure and asserting influence over key transit points in the area. In particular, Russia’s invasion of Ukraine certainly evidenced its willingness to challenge international law, a pattern that could extend to the Arctic as well. Therefore, it is imperative that NATO reconsiders its defense strategy for the High North in order to prevent further destabilization.
A major tool for ensuring stability in Svalbard and the whole of the Arctic territory is to strengthen Diplomatic Engagement. It is pivotal that Norway and its Western allies reinforce multilateral dialogue via the Arctic Council in an attempt to prevent a conflict, while parallelly making Russia’s continued participation in governance processes regarding the Arctic dependent on adherence to the obligation established under the treaty and international law. Moreover, Norway should ensure compliance with the Svalbard Treaty by coordinating with other European allies while avoiding unnecessary provocations. Beyond diplomatic efforts, it is paramount to enhance NATO’s strategy in the Arctic. This can be achieved by increasing NATO’s presence in the High North through joint military exercises and surveillance while additionally improving the strategic and military infrastructure of Norway and other Arctic states to further attempt to deter aggression. Notwithstanding potential efforts to exert diplomatic and military pressure on Russia, it is necessary to also use economic leverage to avoid further escalation. This can be achieved by considering targeted sanctions on individuals and entities involved in Arctic aggression while exploring economic engagement strategies that regulate Russian participation in the Arctic. Furthermore, by enhancing its own economic presence in Svalbard and supporting industries and infrastructure in the region, Norway could reaffirm its sovereignty and boost its economy as well as reduce Svalbard’s reliance on Russian economic activities.
The Arctic is no longer a remote periphery but a central stage for geopolitical competition, where economic, strategic, and military interests are increasingly intertwined. Russia’s growing presence in Svalbard poses a direct challenge to international law and regional stability and, thus, requires a firm yet carefully coordinated response. The European Union, NATO, and Arctic stakeholders must take decisive action to uphold the principles of the Svalbard Treaty, ensuring that Russia does not exploit legal ambiguities to expand its influence unchecked. A balanced approach, which combines diplomatic engagement, strategic deterrence, and targeted economic measures, coulb be essential to maintaining stability in the region. By proactively addressing these challenges, the international community can safeguard the Arctic’s future and prevent it from becoming the next major geopolitical flashpoint.
By The European Institute for International Relations